Mexican economy: history, structure, main sectors
Mexico, one of the largest and most influential countries in Latin America, plays a significant role in the regional and global economy. With its rich cultural heritage, diverse natural resources and dynamic economic activities, it has attracted the attention of the world community. Mexico’s economy is an important factor in global trade and also influences the stability and development of Latin America as a whole.

From its founding until today, Mexico’s economy has traveled a long path of development, experiencing various historical periods, including its colonial past, political crises and economic reforms. Today, it is a mixed economy with developed industrial, agricultural, service and tourism sectors.
A key aspect of the importance of the Mexican economy is its role in world trade. Mexico is the largest trading partner of the United States and also trades extensively with other countries in Latin America, Europe, and Asia. Due to its strategic position and membership in various international trade organizations, such as the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and free trade treaties with the European Union, Mexico has access to a variety of markets and investment opportunities.
Moreover, Mexico’s economy plays an important role in the stability of the region. The country is one of the largest economic leaders in Latin America and influences the economic development of neighboring countries. The successes or failures of the Mexican economy have a direct reflection on neighboring countries, and therefore, its economic well-being is of strategic importance to the entire region.
Overall, Mexico’s economy is an integral part of the world economic system and has a significant impact on its development and stability. Later in the article we will look at the history of the Mexican economy, its structure and main sectors, as well as the challenges and prospects for its development.
Economic history of Mexico: from ancient civilizations to modern times
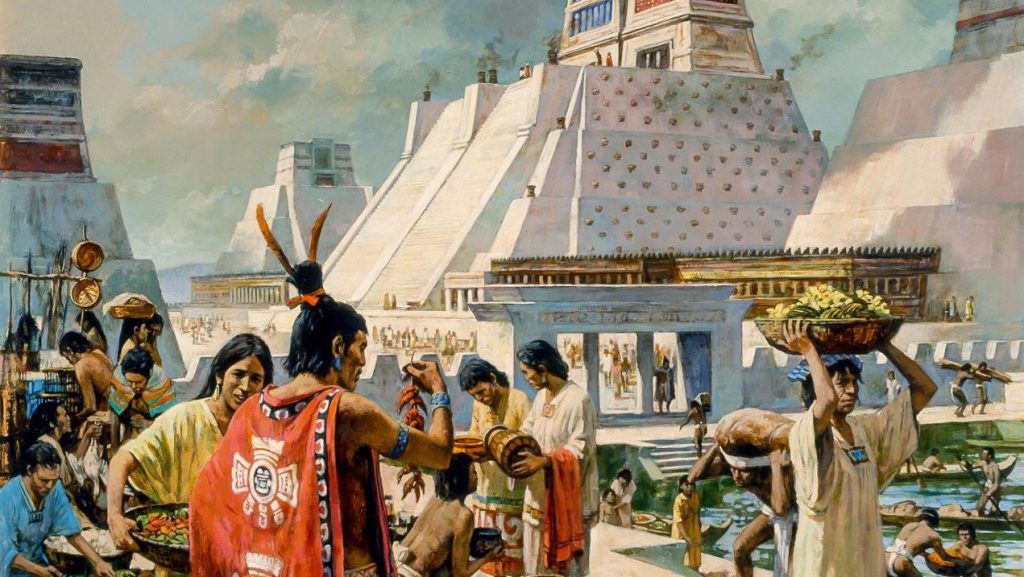

The economic history of Mexico represents a long and varied path of development, from ancient civilizations to modern times. This path has been dotted with various events, including periods of prosperity, colonial rule, revolution and economic reform. Let us review the major stages of this history.
Ancient civilizations: Maya, Aztecs and Toltecs
The ancient Maya, Aztecs, and Toltecs were the first prominent civilizations to emerge in what is now Mexico. Their economy was based on agriculture, crafts, trade, and exchange systems. The Maya developed sophisticated agricultural techniques such as terraced crops and canal irrigation systems. The Aztecs possessed a widespread system of exchange, including the use of coca as a currency.
Colonial period and Spanish domination
After the Spanish conquest in the 16th century, the Mexican economy underwent profound changes. The Spanish conquerors introduced a system of forced labor and exploitation of local resources, which led to the economic exploitation of the local population and the enrichment of the crown. The export of silver from Mexican mines became a major source of income for the Spanish empire.
Revolution and reform in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries
In the nineteenth century, Mexico underwent a series of revolutions and uprisings that greatly affected its economy. One of the key events was the Mexican Revolution (1910-1920), which led to the establishment of new political, economic, and social systems. Important reforms such as land reform and nationalization of the oil industry were implemented to improve the economic justice and self-determination of the country.
Modern Economic History
Mexico’s modern history has seen steps toward economic development and modernization. Economic reforms to liberalize trade and attract foreign investment have contributed to the growth of industry, services, and tourism. The influence of national corporations such as PEMEX (the national oil company) and Cemex (the largest cement producer) play an important role in the country’s economy.
These stages and events illustrate the rich history of Mexico’s economy, from its ancient roots to the present. The country continues to develop and improve, and its economy remains a key factor both regionally and globally.
Structure of the Mexican economy: main sectors and indicators

Mexico is a country with a diverse economy in which agriculture, industry and services play a key role. Let’s take a look at the main sectors of the Mexican economy and their geographical distribution, as well as the main economic indicators.
Agriculture
Agriculture plays a significant role in Mexico’s economy, although its share in the country’s total GDP has been declining year after year. Currently, agriculture accounts for about 4% of Mexico’s total GDP. However, this does not reflect its key importance to the country, as it provides food security and employment to a large part of the population.
Agriculture in Mexico is mainly concentrated in the central and southern regions of the country, where the climate and soils provide more suitable conditions for agricultural activities. Some of the key regions of agriculture in Mexico include the Bajio Valley, the states of Sinaloa, San Luis Potosí, and Oaxaca.
An important aspect of Mexican agriculture is its diversity. Mexico produces a wide range of crops including maize, beans, sugar cane, agave, avocados, tomatoes, peppers, as well as citrus fruits and more. Due to the variety of climates throughout the country, Mexico has the ability to grow many types of crops year-round.
Agriculture in Mexico faces a number of challenges and prospects. Some of the main challenges include the lack of utilization of modern technology in production, instability in agricultural prices, and problems with water resources and land reform. However, despite these challenges, Mexican agriculture has significant development prospects, especially with the proper utilization of new technologies and improved infrastructure. The country is also working hard to increase agricultural exports and access to global markets.
There are a significant number of jobs in Mexico’s agriculture sector for both residents and non-residents of the country. This field offers opportunities for work both on farms and plantations as well as in management and technical support.
For residents of Mexico, agriculture presents a wide range of employment opportunities as seasonal or permanent workers on farms and plantations. Jobs can involve various aspects of production, including seeding, plant care, harvesting, livestock management, and more. In addition, agriculture requires specialists in various fields such as agronomists, veterinarians, water engineers, and agricultural mechanization, offering additional employment opportunities.
Jobs in agriculture are also available for non-residents of Mexico. Many farms and plantations hire temporary workers from other countries for seasonal jobs such as harvesting fruits, vegetables, or flowers. In addition, the Mexican government provides programs for temporary employment of foreign workers, such as the H-2A temporary agricultural employment program, which allows workers from other countries to come to work seasonally in agriculture.
Agricultural jobs in Mexico can provide a variety of benefits such as wages, on-farm room and board, and access to health insurance and other benefits. It is important to note that jobs and working conditions can vary depending on the region of the country, the type of farm or plantation, and the time of year.
Industry
Industry is a key sector of Mexico’s economy, including the production of automobiles, electronics, textiles, food products, and other goods. Major industrial regions include northern states such as Chihuahua, Sonora, and Nuevo León, and central states such as Mexico City and Guanajuato.
Metallurgy: The metallurgical industry in Mexico is an important sector and includes the production of steel, aluminum and other metals. It plays a key role in the construction, automotive and energy industries. Industrial complexes are located in various regions of the country, including the states of Mexico, Chihuahua and Michoacán.
Automotive Industry: Mexico is one of the largest automobile manufacturers in the world. Many of the world’s automakers such as General Motors, Ford, Volkswagen, Toyota and Nissan have plants here. The main automobile plants are located in the states of Mexico City, Guanajuato and Puebla.
Textile industry: Mexico’s textile industry is an important part of the country’s economy. It includes the production of textiles, clothing, footwear and textile materials. The main textile centers are located in the states of Puebla, Oaxaca, and Guanajuato.
Food industry: Mexico’s food industry is one of the largest in the region and includes the production of food, beverages and tobacco products. It occupies a significant share of the country’s exports. The main food production facilities are located in different regions of the country, including the states of Jalisco, Guerrero, and Michoacán.
Mexico’s industry has both prospects and challenges. Among the prospects are export growth, cooperation with international companies, technology modernization and infrastructure development. However, there are also challenges, such as competition in the global marketplace, instability in the domestic political and economic climate, and problems with infrastructure and access to capital.
For residents of Mexico, the industry provides ample employment opportunities in a variety of fields including manufacturing, engineering, logistics and management. There are also employment opportunities for non-residents, especially in international companies that are actively developing their businesses in Mexico.
Services
The service sector also plays a significant role in Mexico’s economy. This includes financial services, tourism, transportation, telecommunications, and trade. Tourism is a major service industry and an important source of foreign exchange earnings for the country.
Tourism: Tourism is one of the main sources of income for Mexico. The country attracts millions of tourists every year due to its beautiful beaches, historical sites, cultural events and unique cuisine. Tourism accounts for a significant portion of Mexico’s GDP and is an important source of jobs, especially in regions popular with tourists such as Cancun, Mexico City, Puerto Vallarta, and Cabo San Lucas.
Finance: Mexico’s financial sector also plays an important role in the country’s economy. Banking, insurance, investments, and other financial services provide a wide range of services to corporate clients and the public. Financial activities are concentrated in the country’s major cities such as Mexico City, Monterrey, and Guadalajara.
Information Technology: The information technology industry is growing rapidly in Mexico. Software development, outsourcing, digital marketing and other technology companies are actively expanding their presence in the country. Many are located in Mexico City, Guadalajara, and Monterrey.
The service sector provides both opportunities and challenges. Opportunities include the expansion of tourism, foreign investment in the financial sector, and the growth of the information technology sector and the digital economy. However, there are also challenges, such as an unstable domestic political and economic environment, as well as cybersecurity challenges and a shortage of skilled professionals.
For residents of Mexico, the service sector offers many job opportunities in various fields such as tourism, banking, information technology and others. There are also opportunities for non-residents to work in the Mexican service sector, especially in international companies and organizations that are actively developing their presence in the country.
Geographic distribution of economic activity

The geographic distribution of economic activity in Mexico has several characteristics that affect the country’s economic dynamics. It is important to understand these factors in order to determine development and investment strategies.
North and South: Mexico is characterized by a north-south division of economic activity. Northern regions, including cities like Monterrey and Tijuana, are industry-oriented, including automobile manufacturing, electronics, and textiles. These regions also have high levels of infrastructure and industrial development.
Central Regions: The central parts of the country, such as Mexico City and its environs, are dominated by the financial and commercial sector. Mexico City is the largest financial center in the country and one of the largest in Latin America.
Southern States: The southern regions, including Yucatán and Oaxaca, are mainly specialized in agriculture and tourism. These regions are known for their historical and cultural attractions as well as rich natural resources.
Border Zones: Border regions with the United States are significant to Mexico’s economy due to manufacturing zones, maquiladoras, and trade and transportation across the border.
The geographic distribution of economic activity in Mexico is important because it defines the country’s economic landscape and forms the basis for strategic planning and development. Understanding these characteristics helps government and businesses identify problem areas, as well as identify potential opportunities for growth and investment in different regions. It is also important for balanced development and combating regional inequalities, which contributes to sustainable and inclusive economic progress.
Current state and challenges of the Mexican economy: inflation, unemployment, foreign trade
The current state of the Mexican economy is the subject of attention of both domestic and international economists and analysts. Let’s look at the main aspects of the current state of the Mexican economy: inflation, unemployment, and foreign trade. Consider data for the year 2023:
GDP (Gross Domestic Product): In 2023, Mexico’s GDP was approximately $1.36 trillion. This figure reflects the total value of all goods and services produced in a country over a given period of time and is a key indicator of economic growth.
Inflation: In recent years, Mexico has experienced inflation. According to the Central Bank of Mexico, the inflation rate was about 4.5% in 2023. Causes of inflation include rising oil prices, higher fuel and food costs, and domestic factors such as budget deficits and tax increases.
Unemployment: Mexico’s unemployment rate in 2023 was approximately 3.5%. This rate reflects the percentage of working-age people who are unemployed and is an important indicator for assessing social stability and economic well-being.
Foreign Trade: Mexico plays an important role in world trade due to its strategic geographic location and developed manufacturing base. It is a member of several international trade organizations such as the North American Free Trade Agreement (SNAFTA) and the World Trade Organization (WTO). Export commodities include automobiles, electronics, petroleum and food products.
Investment: In 2023, Mexico’s investment rate was about 24% of GDP. Investment plays a key role in driving economic growth, creating jobs, and increasing productivity.
The issues of inflation, unemployment, and trade deficit pose serious challenges to the Mexican economy. Addressing inflation and unemployment issues, as well as promoting foreign trade, will contribute to stable and sustainable economic growth in Mexico.
Overall, the Mexican economy continues to grow and modernize, attracting the attention of investors and entrepreneurs from around the world. Its variety of industries and geographic diversity make it an attractive destination for business and investment.
Future prospects for the Mexican economy

With globalization, Mexico has significant opportunities to grow and develop its economy. Let’s look at the future prospects for the Mexican economy:
Expanding trade ties:
Mexico can continue to deepen its trade relations with other countries, especially with the United States, its largest trading partner. Further development of international trade could increase exports of Mexican goods and services.
Investing in human capital:
Developing education and upgrading the skills of the labor force are key aspects of stimulating economic growth. Mexico can invest in education, health care, and support for scientific and technological advancement to create competitive human capital.
Stimulating entrepreneurship and innovation:
Promoting entrepreneurship and innovation can foster the emergence of new economic sectors and job creation. Encouraging investment in startups and technological innovation can help improve a country’s competitiveness.
Tax and Legal Reforms:
Mexico can continue to implement tax and legal reforms to create a favorable investment environment. Simplifying tax procedures and improving legal protection for businesses can attract more foreign investment and promote domestic market development.
Development Forecasts:
In the medium to long term, Mexico’s economy may continue to show steady growth. Contributing factors will be the implementation of reforms, improved trade relations with other countries, and the development of infrastructure and human capital.
Overall, Mexico has the potential for further economic development with the right approach to implementing reforms and strategies to stimulate growth. Realizing these prospects could attract more investment, create new jobs and improve the quality of life of the population.
In this context, a moving company can offer its services as a means of supporting and contributing to the development of the Mexican economy. Business and individual relocations can be part of the process of expanding businesses and attracting new investments to the country.
Contact us in any way:
Telephone: (954) 773-9667
E-mail: abs@absoluteinc.org
Website: https://absoluterelocationservices.com





