Alaska Local Cuisine: Recipes and Local Foods
Alaska, the largest by area and one of the most isolated states in the United States, is famous not only for its majestic nature but also for its unique culinary heritage. Located in northwestern North America, Alaska has a rich cultural and historical identity that is reflected in its cuisine.
Traditional Alaskan cuisine, based on local products and indigenous ethical traditions, as well as cultural influences from Russians, Europeans and Asians, is a key element of the state’s cultural heritage. Ethnic diversity and the variety of native flora and fauna have formed a unique culinary tradition that epitomizes the spirit and character of Alaska.
The importance of culinary heritage to Alaska’s culture and society cannot be overemphasized. Not only is it part of the national identity, but it also plays an important role in preserving and transmitting the traditions and historical values of local communities. Cuisine reflects the characteristics of the state’s natural environment, climate, and lifestyle, as well as historical, ethnic, and cultural influences developed over the centuries.
Alaskan Cuisine History

Alaska, with its unique nature and ethnic diversity, has an equally unique culinary tradition that reflects the influence of local flora and fauna, climate, and historical traditions. The history of Alaskan cuisine is rich and varied, and its roots go far back in time.
One of the main features of Alaskan cuisine is its connection to local nature and fisheries. Alaska’s waters, including rivers, lakes and ocean, provide a rich variety of fresh fish specialties such as salmon, cod, flounder and shrimp. Fish is central to many Alaskan dishes and is used extensively in soups, stir-fry and baked dishes.
Another key feature of Alaskan cuisine is the use of local produce and foods gathered from the wild. Honey and berries such as blueberries and cloudberries, as well as wild herbs and greens, are often used in cooking to add a unique flavor and aroma to dishes.
Historically, Alaskan cuisine has been shaped by several ethnic groups that inhabit the region. These include Native Alaskans, Eskimos, and Aleuts, as well as Russians, Americans, and Asians, including Chinese and Japanese. The ethnic traditions and culinary techniques of each of these groups have contributed to the formation of Alaskan cuisine.
The climatic characteristics of the region also play an important role in shaping Alaskan cuisine. The cold climate and long winters favor food preservation and encouraged the development of canning and pickling techniques. Many traditional Alaskan recipes rely on preserved and salted foods such as salted salmon or dried chicken.
Modern Alaskan cuisine maintains a respect for the traditions and cultural heritage of the region. Many dishes, such as grilled salmon and crab cakes, remain popular with locals and tourists. At the same time, modern chefs and culinary professionals are constantly experimenting with traditional recipes, introducing new techniques and ingredients.
Thus, Alaskan cuisine is a unique fusion of local traditions, ethnic influences, and natural resources that define its unique character and importance to Alaskan culture and society.
Main ingredients
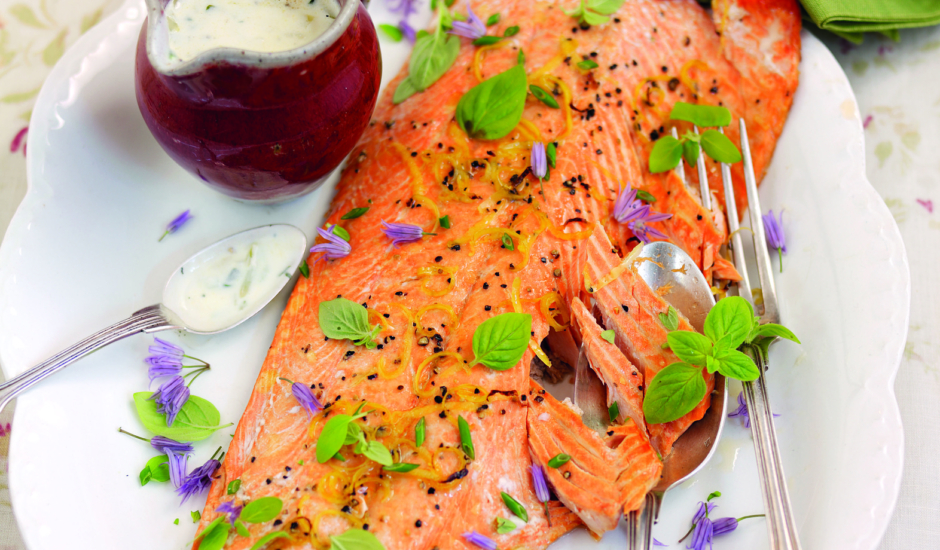

The main ingredients characteristic of Alaskan cuisine reflect the diversity of the local natural conditions and the ethnic traditions of the peoples who inhabit the region.
Salmon is perhaps one of the best known and most important ingredients in Alaskan cuisine. Salmon is not only a popular dish for the locals, but also a symbol of the region. It has a unique flavor and nutritional properties. Salmon in Alaska is found in various forms: fresh, smoked, pickled and canned. This product plays a key role in many Alaskan dishes such as grilled, sushi, soups and cutlets.
Another important ingredient in Alaskan cuisine is crab. Alaska is famous for its seafood, and crab is one of them. Crabs, which live in the cold waters of Alaska, are characterized by tender meat and rich flavor. Crab legs, crab cakes and crab soups are popular dishes in restaurants and home cooking.
Bering lobster is another delicacy characteristic of Alaskan cuisine. This species of crustacean thrives well in Alaska’s marine waters and is an important source of protein and micronutrients for locals. Bering lobster is widely used in a variety of dishes including soups, salads, and crawfish tails that are grilled or baked in the oven.
Cranberries and blueberries are typical berries found in Alaskan nature and are widely used in local cooking. They add a fresh and sour flavor to various dishes such as soursels, compotes, desserts and sauces. Cranberries and blueberries are often used as an ingredient in casseroles, pies and marmalades.
In addition to these main ingredients, honey, seaweed, venison, seafood, and wild herbs and vegetables are also commonly used in Alaskan cuisine. Each of these products plays its own unique role in shaping the authentic flavor and atmosphere of Alaskan cuisine, which still retains its uniqueness and appeal.
Traditional dishes and recipes
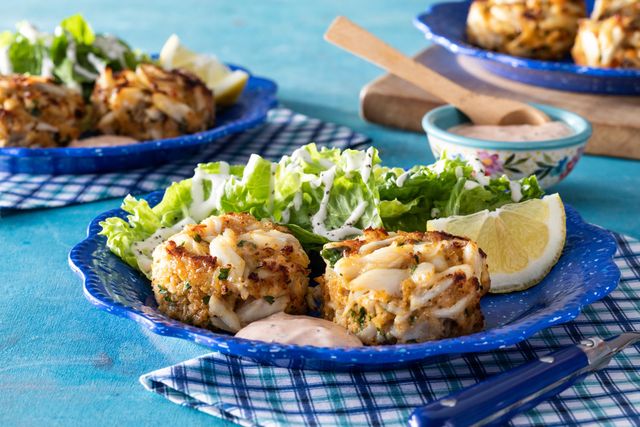

The history of Alaskan cuisine is rich and varied, and its dishes reflect the influences of the different ethnic groups that have settled the land over the centuries.
- Grilled salmon: Fresh salmon was a major food source for local Aboriginal people, including Athabaskans, Tlingits, and Eskimos. They used a variety of methods to prepare it, including grilling and smoking. The arrival of European colonists introduced new cooking methods such as marinades and sauces.
- Crab Cakes: Alaska is famous for its extensive crab stocks. Crab cakes were probably influenced by the culinary traditions of American colonists and European immigrants who came to Alaska in the 19th century.
- Venison in sauce: Venison was a major food source for local Aboriginal people. It was used to prepare a variety of dishes including stews and roasts. This meat was not only a food but also a symbol of community and tradition for Alaska Native people.
- Blueberry pancakes: Blueberry pancakes are a combination of Russian and Scandinavian cuisine that came to Alaska with the Russian and Scandinavian colonists. Blueberries, which grow abundantly in the forests of Alaska, were a great addition to this traditional dessert.
- Baked Salmon with Honey and Mustard: This dish combines the influence of indigenous peoples who used salmon as a primary food source with the culinary techniques of European immigrants. Honey and mustard may have been introduced by Europeans and Americans through cultural exchange.
- Beaver Meat Soup: This dish probably has roots in Alaska Native cuisines. Beavers were an important food source for local people, and their meat was used to prepare a variety of dishes, including soups and stews.
Thus, Alaska’s rich culinary heritage has been shaped by the interaction of different cultures and ethnic groups, and each dish has its own unique history and significance to the commonalities of the region.
Culinary traditions of different ethnic groups
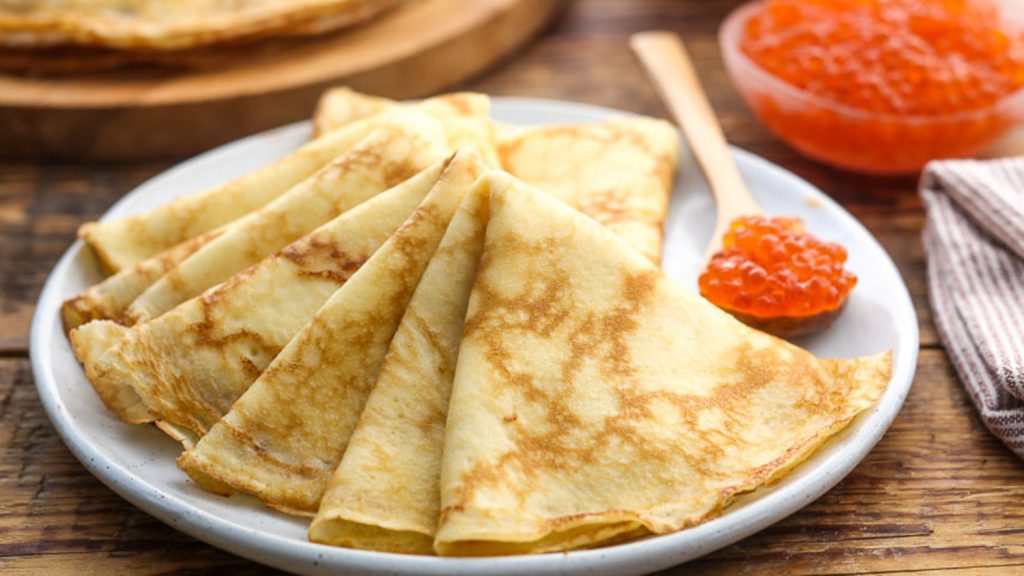

The contributions of various ethnic groups to Alaskan cuisine reflect the richness of the region’s cultural diversity. In this section, we will examine some of the major ethnic groups and their unique culinary traditions.
- Tlingit Indians: The Tlingit ethnic group living in Southeast Alaska has a rich culinary heritage. One of their traditional foods is “halbut,” a large fish that is often cooked on a grill or in an earthen oven pit. They are also known for their recipes using honey, berries and roots.
- Eskimos: An ethnic group of Eskimos living in northern and western Alaska, they depend on hunting marine mammals and fishing. Their traditional cuisine includes meat from walruses, seals, whales, and salmon prepared in a variety of ways: smoking, boiling, frying, and pickles. “Akitlek”, raw sea bass, is also popular among the Eskimos.
- Athabaskans: The Athabaskan ethnic group living in interior Alaska traditionally hunts reindeer meat and fish, which play a key role in their culinary traditions. One famous dish is “pishu,” dried and smoked fish that is then used to prepare various dishes.
- Russian colonists: Russian colonists who arrived in Alaska in the 18th and 19th centuries also had a significant influence on the local cuisine. They brought with them recipes for pancakes, pies, salads, and other dishes that became part of Alaskan cuisine.
- American colonists and emigrants: In the 19th century, Alaska attracted American colonists and emigrants who also contributed to the culinary diversity of the region. They brought with them recipes for pies, baked dishes, and barbecue that became popular in Alaskan cuisine.
Each of these ethnic groups has made unique contributions to Alaskan cuisine, creating a variety of dishes and traditions that reflect the richness of the region’s cultural heritage.
Modern interpretations and new directions
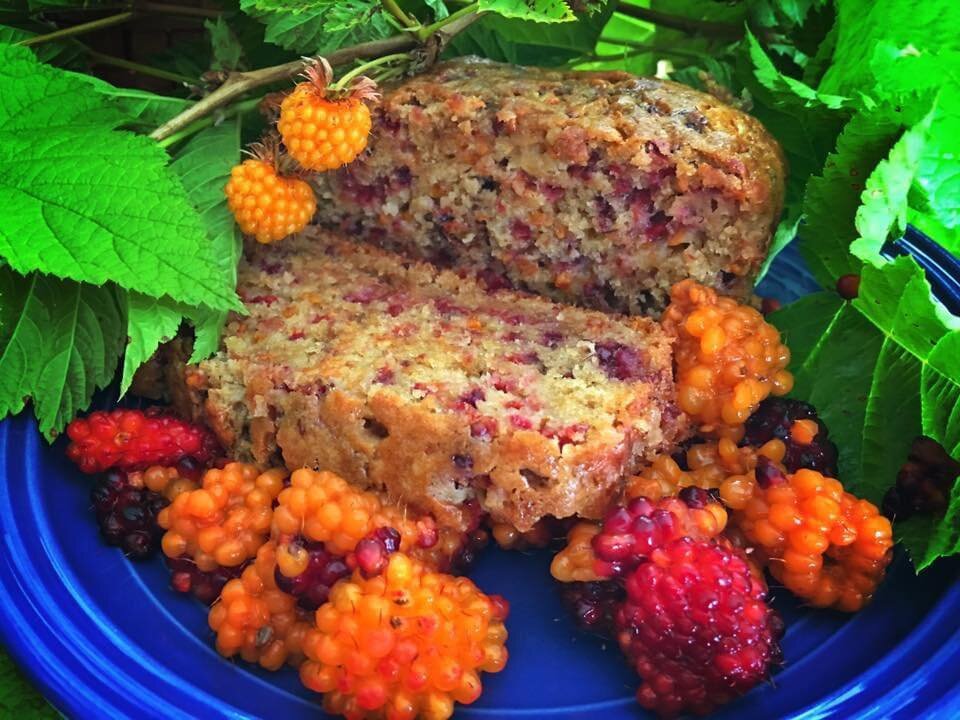

In today’s environment, Alaskan cuisine continues to evolve, retaining its traditional characteristics but also adapting to modern trends and interacting with global culinary culture.
- Innovation in traditional dishes: Today, many Alaskan chefs and culinary professionals are looking for new ways to prepare traditional dishes to give them a more modern look and flavor. For example, the classic “pishu” can now be served as sushi or salad with the addition of fresh vegetables and spices, giving this dish new flavors and textures.
- Local ingredients and sustainable products: With the growing interest in healthy eating and sustainable products, many Alaskan restaurants and cafes have begun to heavily utilize local ingredients and products such as fresh Alaskan fish, seafood, berries, wild herbs and mushrooms. This supports local farming and reduces environmental pressures.
- Fusion cuisine: In recent years, it has become popular to combine traditional Alaskan dishes with elements of other culinary traditions. For example, you may find dishes inspired by Japanese, Mexican, or Italian cuisine, but prepared using local Alaskan ingredients. This approach creates unique and distinctive flavor combinations.
- Culinary Festivals and Events: Culinary festivals and events are held in various regions throughout Alaska where chefs and culinary professionals showcase new recipes, share experiences, and inspire each other’s creativity. This promotes the region’s culinary scene and brings attention to Alaskan cuisine.
- Digitalization of recipes and culinary traditions: With the development of the internet and social media, it has become easier to share recipes and culinary traditions. Many Alaskan recipes are now available in an online format, allowing people from different countries to familiarize themselves with Alaskan cuisine and experiment with its dishes in their own kitchens.
Modern Alaskan cuisine continues to surprise and inspire with its diversity and originality, remaining a key aspect of the region’s cultural heritage.
In the conclusion of this article, we draw attention to the richness and diversity of Alaskan cuisine, which is a unique combination of traditions, cultures, and natural features of this region. We have looked at the history of Alaskan cuisine, its main ingredients, traditional dishes, and the contributions of different ethnic groups to the development of culinary traditions.
This article may be especially useful for those who plan to visit Alaska or are interested in the culinary heritage of this region. It allows you to immerse yourself in the local cuisine, learn about traditional dishes and cooking methods, and understand the influence of nature, climate, and ethnic traditions in shaping Alaska’s culinary identity.
Alaskan cuisine continues to attract attention for its wealth of flavors, traditions, and history. This article aims to emphasize the uniqueness and diversity of Alaskan cuisine and to help readers better understand and appreciate the cultural heritage of this beautiful region. And our moving company is ready to be your reliable partner in moving to Alaska. We offer professional moving services and will help you with a comfortable adjustment in this amazing region.
Contact us in any way:
Telephone: (954) 773-9667
E-mail: abs@absoluteinc.org





